PostgreSQL 子事务日志管理器
本文简要记录一下 PostgreSQL 中有关子事务相关的处理,PostgreSQL 中子事务(pg_subtrans)的管理与事务管理(pg_xact)类似,它存储了每个事务的父事务 ID。它是实现嵌套事务的基本组成部分。主事务(即顶层事务)的父事务 ID 为 InvalidTransactionId,每个子事务都有其直接的父事务 ID。因此,我们可以通过子事务遍历很容易找到父事务 ID,反之则不然。
pg_subtrans 只记录当前已打开的事务,因此无需为崩溃或重启持久化数据。在重启时,PostgreSQL 会将当前获取的页面清零。
页面布局
PostgreSQL 将 pg_subtrans 目录下的文件视为一个 hash 表,可以通过事务的 ID 快速获取其直接的父事务 ID,通过这种方式一直往上遍历可以获取到主事务 ID。
PostgreSQL 将子事务信息按页面进行分块,并且 32 个页面组成一个段文件(即磁盘文件)。由于事务 ID 是 32 位无符号数,因此每个页面可以存储 BLKSZ / sizeof(TransactionId) 个事务的信息。如下图所示,我们采用 8K 的页面,则每个页面可以存储 8192 / 4 = 2048 个事务的信息。例如当前事务 ID 为 741,则我们可以通过 741 * 4 = 0x00000b94 得到其父事务 ID 为 0x000002e4 = 740,同样地,我们可以得到 740 的父事务 ID 为 739,而 739 的父事务 ID 为 0,即 739 是一个主事务,其关系为 741 -> 740 -> 739。
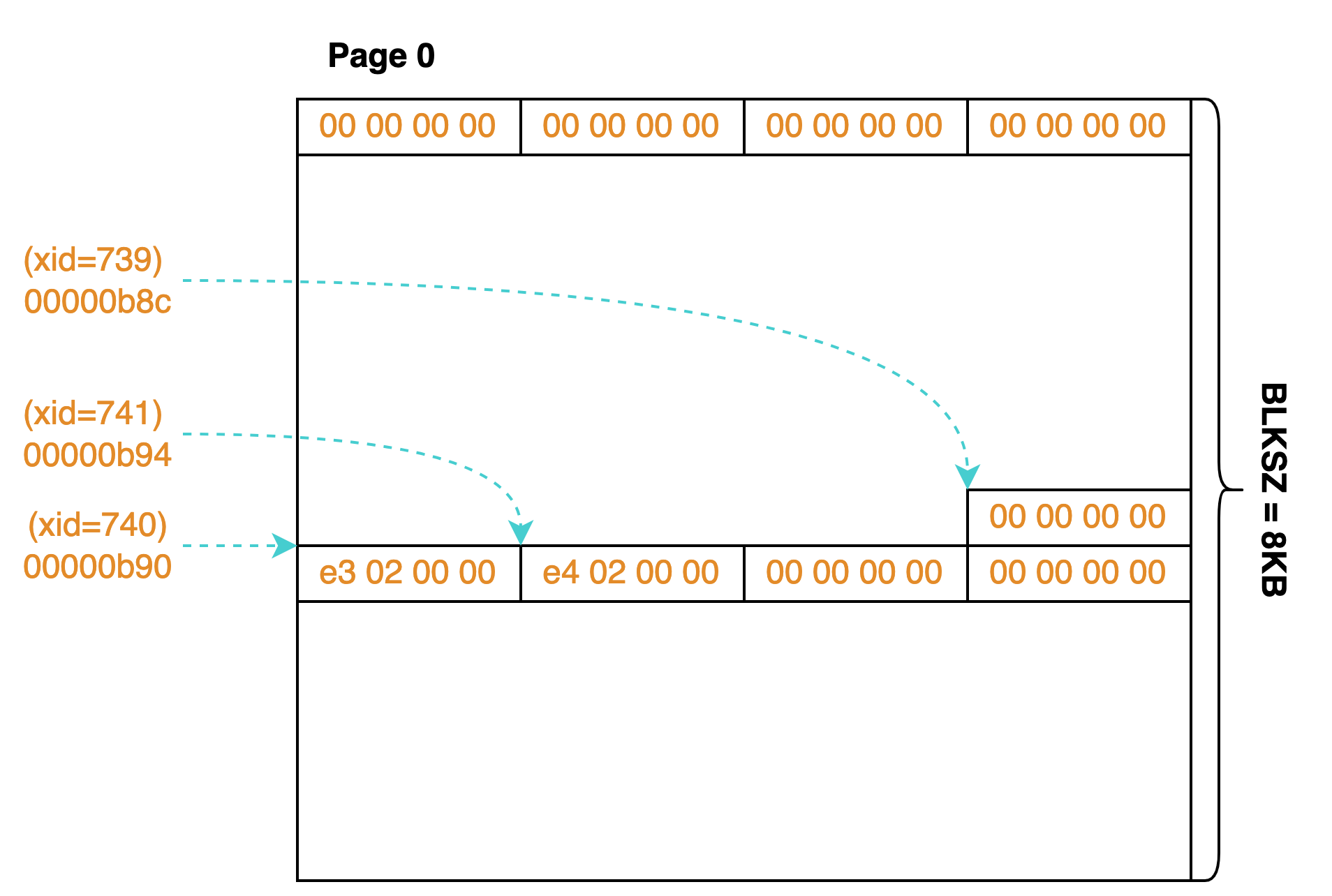
上面的计算中我们忽略了页面编号的计算,子事务管理器提供了 TransactionIdToPage 和 TransactionIdToEntry 宏来帮助计算页面号和页面偏移量,其定义如下所示:
1 | /* We need four bytes per xact. */ |
代码逻辑
PostgreSQL 使用子事务来实现 SAVEPOINT 功能,内部则使用TransactionStateData 结构来描述事务的状态。下面将结合实际情况分析一下子事务的工作原理。首先,使用下面的命令创建示例表。
1 | CREATE TABLE tbl(id int, info text); |
当我们使用 BEGIN 开启事务时,它将调用 BeginTransactionBlock() 函数将 TransactionState->blockState 设置为 TBLOCK_BEGIN 用以表明我们正式进入一个事务块,当执行完 BEGIN 时,finish_xact_command() 函数将调用 CommitTransactionCommand 函数切换 TransactionState->blockState 状态为 TBLOCK_INPROCESS 以表明我们事务块正在运行中。
1 | exec_simple_query |
现在我们在执行下面的语句插入一条记录。
1 | INSERT INTO tbl VALUES (1, 'A'); |
由于这是当前事务中的第一次修改,因此,heap_insert() 函数将调用 GetCurrentTransactionId() 来获取一个事务 ID,如果当前事务已经分配了事务 ID,则直接返回,否则调用 AssignTransactionId() 分配一个新的事务 ID(需要在 XidGenLock 获得 LW_EXCLUSIVE 锁),并保存到 TransactionState->fullTransactionId 中。
1 | exec_simple_query |
接下来,我们通过 SAVEPOINT s1 创建一个子事务(保存点),函数 DefineSavepoint() 将t通过 PushTransactoin() 函数新建一个子事务状态对象,并将当前的事务对象压栈,随后,将新建的子事务对象设置为当前事务对象。当执行完 DefineSavepoint() 函数之后,其事务状态信息如下图所示:
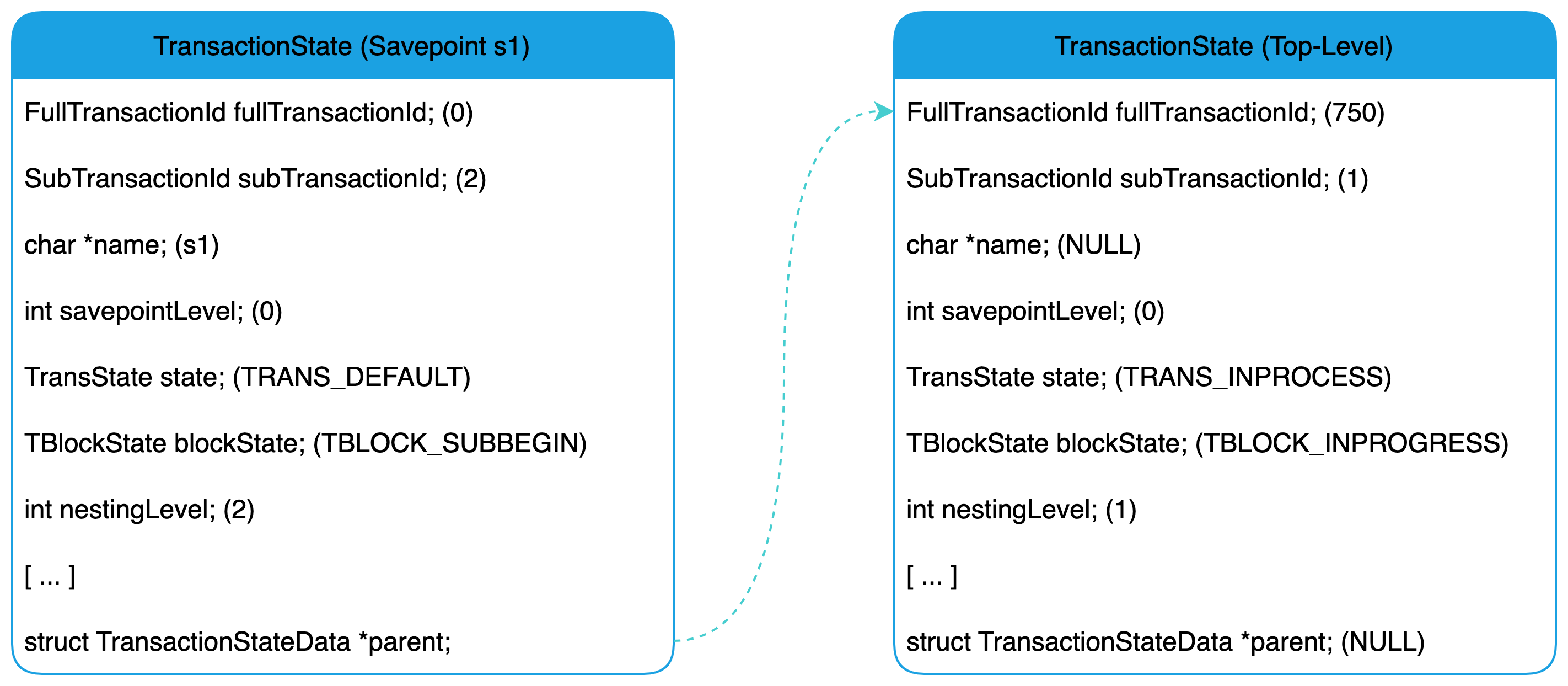
注意: PostgreSQL 一个事务最大支持 2^32 - 1 个子事务。
紧接着,SAVEPOINT s1 语句完成需要调用 CommitTransactionCommand 函数提交,由于当前需要开启子事务,因此 CommitTransactionCommand 函数将调用 StartSubTransaction() 函数进入到子事务状态。最后,事务状态信息如下图所示:
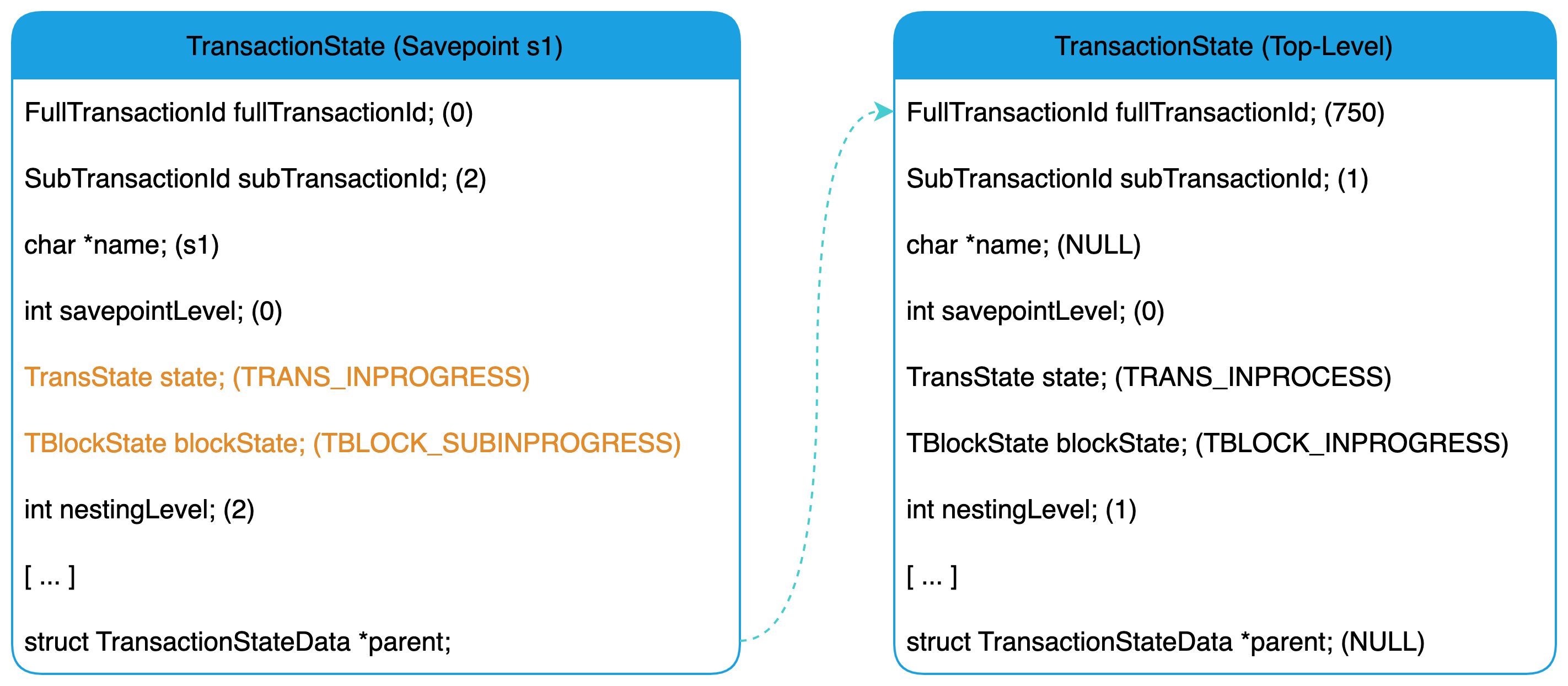
SAVEPOINT 语句的执行流程如下所示:
1 | exec_simple_query |
现在,我们下面的语句在子事务中插入一条记录新的记录。
1 | INSERT INTO tbl VALUES (2, 'B'); |
其整体的执行流程与主事务的大致相同,不同在于获取事务 ID 之后的处理方式。当前事务状态的父事务不为空,因此,该事务为子事务,在调用 GetNewTransactionId() 获得事务 ID 之后,它将调用 SubTransSetParent() 函数在 pg_subtrans 中记录父事务的事务 ID。当执行完插入后,事务状态信息如下图所示(更新了子事务状态的 FullTransactionId 字段):
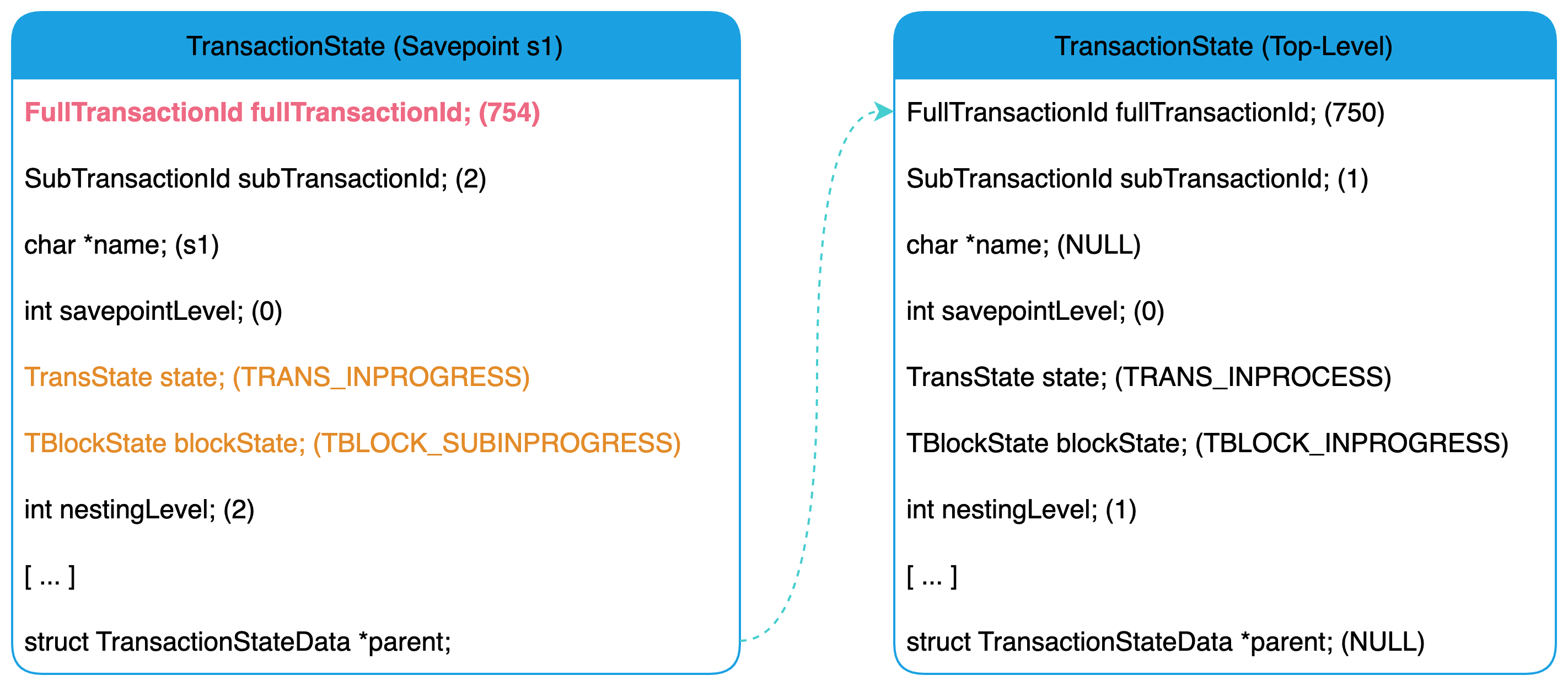
其执行流程如下所示:
1 | exec_simple_query |
SubTransSetParent() 函数为每个子事务记录其直接父事务的事务 ID,其代码如下所示:
1 | /* |
它根据子事务的 ID 获取到对应的页面编号和页内偏移,随后读取相应的页面并将父事务 ID 写入,此时的信息仅在共享内存中,通过 CHECKPOINT 可以将其刷盘。
最后,我们来看看事务的提交过程,当我们执行 COMMIT 时,其执行流程如下所示:
1 | exec_simple_query |
CommitTransactionCommand 函数将循环执行 CommitSubTransaction() 函数来提交子事务;随后,如果是需要提交主事务,则调用 CommitTransaction() 函数进行提交(这里面涉及到了 WAL 日志以及 CLOG 相关的更新,感兴趣的朋友可以去看看)主事务。
如果我们执行 CHECKPOINT,那么我们在 $PGDATA/pg_subtrans 目录下可以看到上述子事务的相关信息。

0x00000bc8 对应的事务 ID 为 int(0xbc8) / 4 = 754,而他的父事务 ID 为 0x02ee = 750,750 事务在 0 号页面的 hex(750 * 4) = 0xbb8,全为 0,因此,事务 750 是主事务,这与上面的实际情况一致。
到此,关于 PostgreSQL 的子事务基本上就了解的差不多了,这部分内容其实相对还是比较简单的,pg_xact 的内容就要比 pg_subtrans 稍微复杂一些。
参考
[1] https://www.postgresql.org/docs/14/sql-begin.html
[2] https://www.postgresql.org/docs/14/sql-checkpoint.html
[3] https://www.postgresql.org/docs/14/sql-commit.html
[4] https://www.postgresql.org/docs/14/sql-savepoint.html
[5] https://github.com/postgres/postgres/tree/REL_14_5
一富翁问“薑”字如何写,对以草字头,次一字,次田字,又一字,又田字,又一字。
其人写草壹田壹田壹,写讫玩之,骂曰:“天杀的,如何诳我,分明作耍我造成一座塔了。”