构建简单的数据库
使用 C 语言从头实现类 sqlite 数据库
10 - 叶子节点分裂
我们的 B-Tree 感觉不像只有一个节点的树。为了解决这个问题,我们需要一些代码将叶节点分成两部分。然后,我们需要创建一个内部节点作为两个叶节点的父节点。
基本上,我们这篇文章的目标是从下图出发:
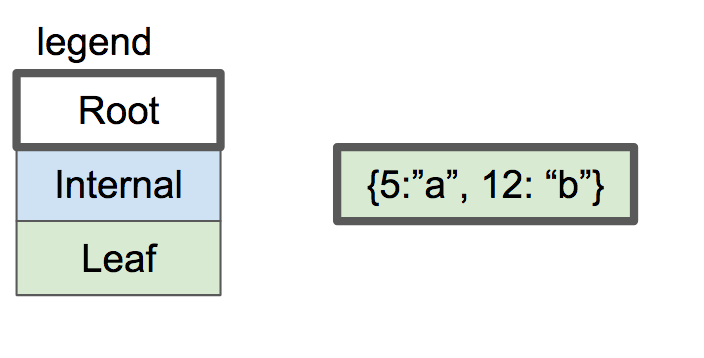 |
到下图:
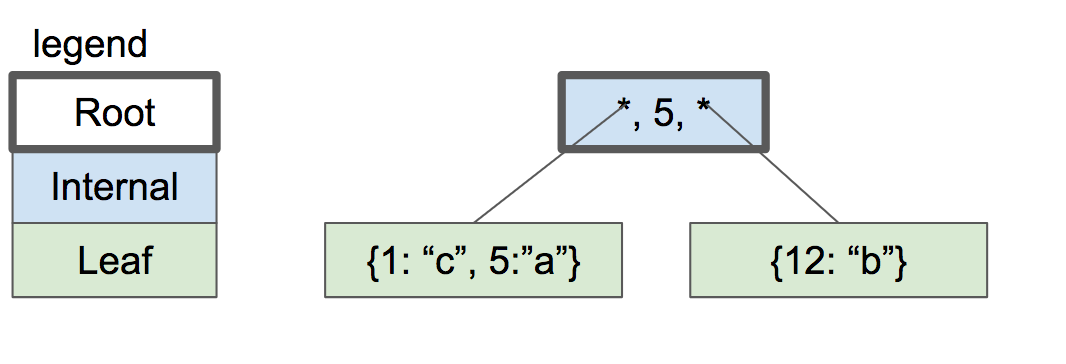 |
首先,让我们移除对完整叶节点的错误处理:
uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
if (num_cells >= LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS) {
/* Node full */
- printf("Need to implement splitting a leaf node.\n");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ leaf_node_split_and_insert(cursor, key, value);
+ return;
}
uint32_t num_cells = (*leaf_node_num_cells(node));
uint32_t key_to_insert;
- if (num_cells >= LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS) {
- return EXECUTE_TABLE_FULL;
- }
-
row_to_insert = &statement->row_to_insert;
key_to_insert = row_to_insert->id;
cursor = table_find(table, key_to_insert);
分裂算法
简单的部分结束了。这是我们需要做的事情的描述 SQLite 数据库系统:设计与实现
If there is no space on the leaf node, we would split the existing entries residing there and the new one (being inserted) into two equal halves: lower and upper halves. (Keys on the upper half are strictly greater than those on the lower half.) We allocate a new leaf node, and move the upper half into the new node.
让我们获取旧节点的句柄并创建新节点:
+void
+leaf_node_split_and_insert(Cursor *cursor, uint32_t key, Row *value)
+{
+ /*
+ * Create a new node and move half the cells over.
+ * Insert the new value in one of the two nodes.
+ * Update parent or create a new parent.
+ */
+
+ void *old_node = get_page(cursor->table->pager, cursor->page_num);
+ uint32_t new_page_num = get_unused_page_num(cursor->table->pager);
+ void *new_node = get_page(cursor->table->pager, new_page_num);
+
+ initialize_leaf_node(new_node);
接下来,将每个单元格复制到新位置:
+ /*
+ * All esisting keys plus new key should be divided
+ * evenly between old (left) and new (right) nodes.
+ * Starting from the right, move each key to correct position.
+ */
+ for (int32_t i = LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS; i >= 0; i--) {
+ uint32_t index_within_node;
+ void *destination;
+ void *destination_node;
+
+ if (i >= LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT) {
+ destination_node = new_node;
+ } else {
+ destination_node = old_node;
+ }
+
+ index_within_node = i % LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+ destination = leaf_node_cell(destination_node, index_within_node);
+
+ if ((uint32_t) i == cursor->cell_num) {
+ serialize_row(value, destination);
+ } else if ((uint32_t) i > cursor->cell_num) {
+ memcpy(destination, leaf_node_cell(old_node, i - 1), LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE);
+ } else {
+ memcpy(destination, leaf_node_cell(old_node, i), LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE);
+ }
+ }
更新每个节点标头中的单元格计数:
+ /* Update cell count on both leaf nodes. */
+ *(leaf_node_num_cells(old_node)) = LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+ *(leaf_node_num_cells(new_node)) = LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT;
然后我们需要更新节点的父节点。如果原始节点是根节点,则它没有父节点。在这种情况下,创建一个新的根节点作为父节点。现在我要把另一个分支剪掉:
+ if (is_node_root(old_node)) {
+ return create_new_root(cursor->table, new_page_num);
+ } else {
+ printf("Need to implement updating parent after split\n");
+ exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ }
+}
分配新页面
让我们回过头来定义一些新的函数和常量。当我们创建一个新的叶子节点时,我们通过函数 get_unused_page_num() 来决定放在那个页面中:
+/*
+ * Until we start recycling free pages, new pages will always
+ * go onto the end of the database file.
+ */
+uint32_t
+get_unused_page_num(Pager *pager)
+{
+ return pager->num_pages;
+}
现在,我们假设在一个有 N 个页面的数据库中,第 0 到 N-1 也已经被分配。因此,我们总是可以为新的页面分配页号 N。最终,在我们实现了删除之后,一些页面可能会变成空的,它们的页号也没有使用。为了更有效率,我们可以重新分配这些空闲的页面。
叶节点大小
为了保持树的平衡,我们在两个新节点之间均匀地分配 cell。如果一个叶子节点可以容纳 N 个 cell,那么在分裂的过程中,我们需要在两个节点之间分配 N+1 个 cell(N 个原 cell 加一个新的 cell)。如果 N+1 是奇数,我就选择左节点来获得一个以上的 cell。
+const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT = (LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS + 1) / 2;
+const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT =
+ (LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS + 1) - LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT;
创建一个新的根节点
以下是 SQLite 数据库系统如何解释创建新根节点的过程:
Let N be the root node. First allocate two nodes, say L and R. Move lower half of N into L and the upper half into R. Now N is empty. Add 〈L, K,R〉 in N, where K is the max key in L. Page N remains the root. Note that the depth of the tree has increased by one, but the new tree remains height balanced without violating any B+-tree property.
此时,我们已经分配了右孩子并将上半部分移入其中。我们的函数将右孩子作为输入并分配一个新页面来存储左孩子。
+void
+create_new_root(Table *table, uint32_t right_child_page_num)
+{
+ /*
+ * Handle splitting the root.
+ * Old root copied to new page, becomes left child.
+ * Address of right child passed in.
+ * Re-initialize root page to contain the new root node.
+ * New root node points to two children.
+ */
+ uint32_t left_child_max_key;
+ void *root = get_page(table->pager, table->root_page_num);
+ void *right_child = get_page(table->pager, right_child_page_num);
+ uint32_t left_child_page_num = get_unused_page_num(table->pager);
+ void *left_child = get_page(table->pager, left_child_page_num);
旧的根被复制到左孩子,所以我们可以重用根页面:
+ /* Left child has data copied from old root. */
+ memcpy(left_child, root, PAGE_SIZE);
+ set_node_root(left_child, false);
最后,我们将根页面初始化为具有两个子节点的新内部节点。
+ /* Root node is a new internal node with one key and two children. */
+ initialize_internal_node(root);
+ set_node_root(root, true);
+ *internal_node_num_keys(root) = 1;
+ *internal_node_child(root, 0) = left_child_page_num;
+ left_child_max_key = get_node_max_key(left_child);
+ *internal_node_key(root, 0) = left_child_max_key;
+ *internal_node_right_child(root) = right_child_page_num;
+}
内部节点格式
现在我们终于要创建一个内部节点了,我们必须定义它的布局。它从公共页头开始,然后是它包含的键数,然后是它最右边的子项的页码。内部节点总是比键多一个子指针。额外的子指针存储在页头中。
+/*
+ * Internal Node Header Layout
+ */
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE;
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_OFFSET =
+ INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET + INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE;
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_HEADER_SIZE = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE +
+ INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE + INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_SIZE;
主体是一个由 cell 组成的数组,其中每个 cell 包含一个子指针和一个键。每个键都应该是其左侧子项中包含的最大键。
+/*
+ * Internal Node Body Layout
+ */
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_KEY_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_CELL_SIZE =
+ INTERNAL_NODE_KEY_SIZE + INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE;
基于这些常量,内部节点的布局如下所示:
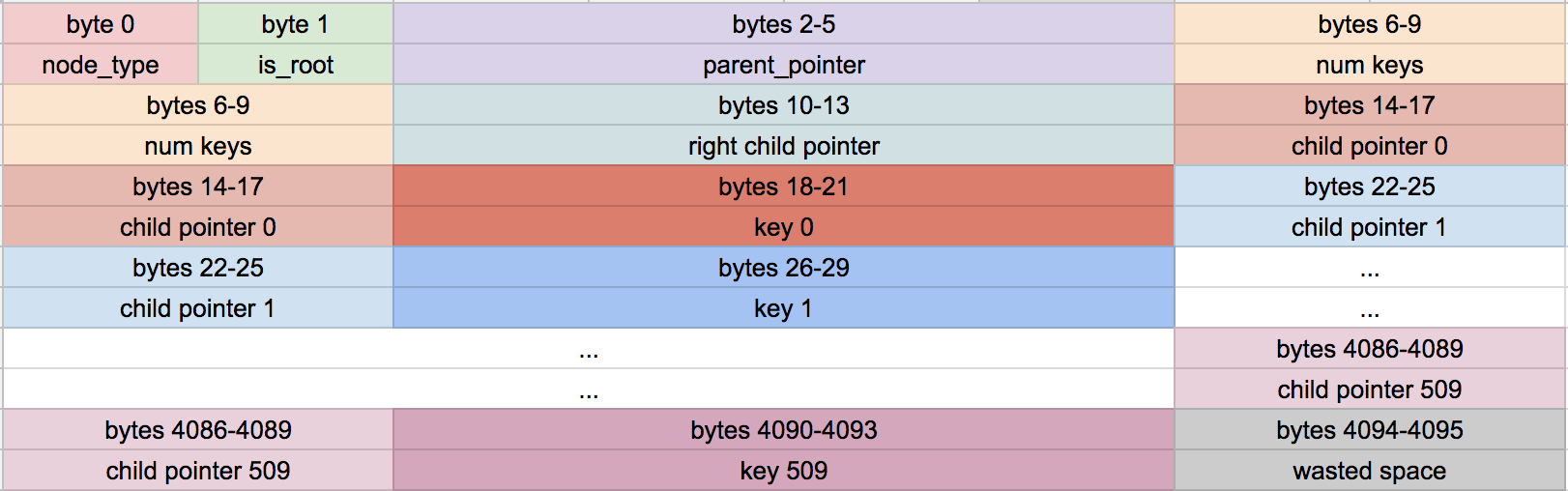 |
注意我们巨大的分支因子。因为每个子指针/键对都很小,我们可以在每个内部节点中放置 510 个键和 511 个子指针。这意味着我们永远不必遍历树的许多层来找到给定的键!
| # internal node layers | max # leaf nodes | Size of all leaf nodes |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 511^0 = 1 | 4 KB |
| 1 | 511^1 = 512 | ~2 MB |
| 2 | 511^2 = 261,121 | ~1 GB |
| 3 | 511^3 = 133,432,831 | ~550 GB |
实际上,由于页头、键和浪费的空间,我们无法为每个叶子节点存储完整的 4KB 数据。但我们只需从磁盘加载 4 页,就可以搜索大约 500GB 的数据。这就是为什么 B-tree 是数据库中有用的数据结构。
以下是读取和写入内部节点的方法:
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_num_keys(void *node)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_right_child(void *node)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_OFFSET;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_cell(void *node, uint32_t cell_num)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_HEADER_SIZE + cell_num * INTERNAL_NODE_CELL_SIZE;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_child(void *node, uint32_t child_num)
+{
+ uint32_t num_keys = *internal_node_num_keys(node);
+ if (child_num > num_keys) {
+ printf("Tried to access child_num %d > num_keys %d\n", child_num, num_keys);
+ exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ } else if (child_num == num_keys) {
+ return internal_node_right_child(node);
+ }
+
+ return internal_node_cell(node, child_num);
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_key(void *node, uint32_t key_num)
+{
+ return internal_node_cell(node, key_num) + INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE;
+}
对于内部节点,最大键始终是其右键。对于叶节点,它是最大索引处的键:
+uint32_t
+get_node_max_key(void *node)
+{
+ switch (get_node_type(node)) {
+ case NODE_INTERNAL:
+ return *internal_node_key(node, *internal_node_num_keys(node) - 1);
+ case NODE_LEAF:
+ return *leaf_node_key(node, *leaf_node_num_cells(node) - 1);
+ }
+}
跟踪根节点
我们最终在公共节点头中使用 is_root 字段。回想一下,我们使用它来决定如何拆分叶节点:
if (is_node_root(old_node)) {
return create_new_root(cursor->table, new_page_num);
} else {
printf("Need to implement updating parent after split\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
下面是获取和设置根节点的函数:
+bool
+is_node_root(void *node)
+{
+ uint8_t value = *((uint8_t *) (node + IS_ROOT_OFFSET));
+ return (bool) value;
+}
+
+void
+set_node_root(void *node, bool is_root)
+{
+ uint8_t value = is_root;
+ *((uint8_t *) (node + IS_ROOT_OFFSET)) = value;
+}
内部节点和叶节点这两种类型的节点默认将 is_root 设置为 false:
void
initialize_leaf_node(void *node)
{
set_node_type(node, NODE_LEAF);
+ set_node_root(node, false);
*leaf_node_num_cells(node) = 0;
}
+void
+initialize_internal_node(void *node)
+{
+ set_node_type(node, NODE_INTERNAL);
+ set_node_root(node, false);
+ *internal_node_num_keys(node) = 0;
+}
我们应该在创建表的第一个节点时将 is_root 设置为 true:
/* New database file. Initialize page 0 as leaf node. */
void *root_node = get_page(pager, 0);
initialize_leaf_node(root_node);
+ set_node_root(root_node, true);
}
return table;
打印树
为了帮助我们可视化数据库的状态,我们应该更新我们的 .btree 元命令以打印多级树。
我将替换当前的 print_leaf_nodef() 函数。
-void
-print_leaf_node(void* node)
-{
- uint32_t i;
- uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
-
- printf("leaf (size %d)\n", num_cells);
- for (i = 0; i < num_cells; i++) {
- uint32_t key = *leaf_node_key(node, i);
- printf(" - %d : %d\n", i, key);
- }
-}
使用新的递归函数接收任何节点,然后打印它及其子节点。它采用缩进级别作为参数,随着每次递归调用而增加缩紧级别。我还添加了一个小的辅助函数来缩进。
+void
+indent(uint32_t level)
+{
+ uint32_t i;
+ for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+}
+
+void
+print_tree(Pager *pager, uint32_t page_num, uint32_t indentation_level)
+{
+ uint32_t i;
+ uint32_t num_keys;
+ uint32_t child;
+ void *node = get_page(pager, page_num);
+
+ switch (get_node_type(node)) {
+ case NODE_LEAF:
+ num_keys = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
+ indent(indentation_level);
+ printf("- leaf (size %d)\n", num_keys);
+ for (i = 0; i < num_keys; i++) {
+ indent(indentation_level + 1);
+ printf("- %d\n", *leaf_node_key(node, i));
+ }
+ break;
+ case NODE_INTERNAL:
+ num_keys = *internal_node_num_keys(node);
+ indent(indentation_level);
+ printf("- internal (size %d)\n", num_keys);
+ for (i = 0; i < num_keys; i++) {
+ child = *internal_node_child(node, i);
+ print_tree(pager, child, indentation_level + 1);
+
+ indent(indentation_level + 1);
+ printf("- key %d\n", *internal_node_key(node, i));
+ }
+
+ child = *internal_node_right_child(node);
+ print_tree(pager, child, indentation_level + 1);
+ break;
+ }
+}
并更新对 print 函数的调用,传递缩进级别为零。
} else if (strcmp(input_buffer->buffer, ".btree") == 0) {
printf("Tree:\n");
- print_leaf_node(get_page(table->pager, 0));
+ print_tree(table->pager, 0, 0);
return META_COMMAND_SUCCESS;
这是新打印功能的测试用例!
+ it 'allows printing out the structure of a 3-leaf-node btree' do
+ script = (1..14).map do |i|
+ "insert #{i} user#{i} person#{i}@example.com"
+ end
+ script << ".btree"
+ script << "insert 15 user15 person15@example.com"
+ script << ".exit"
+ result = run_script(script)
+
+ expect(result[14...(result.length)]).to match_array([
+ "db > Tree:",
+ "- internal (size 1)",
+ " - leaf (size 7)",
+ " - 1",
+ " - 2",
+ " - 3",
+ " - 4",
+ " - 5",
+ " - 6",
+ " - 7",
+ " - key 7",
+ " - leaf (size 7)",
+ " - 8",
+ " - 9",
+ " - 10",
+ " - 11",
+ " - 12",
+ " - 13",
+ " - 14",
+ "db > Need to implement searching an internal node",
+ ])
+ end
+
新格式稍微简化了一点,所以我们需要更新现有的 .btree 测试:
"db > Executed.",
"db > Executed.",
"db > Tree:",
- "leaf (size 3)",
- " - 0 : 1",
- " - 1 : 2",
- " - 2 : 3",
+ "- leaf (size 3)",
+ " - 1",
+ " - 2",
+ " - 3",
"db > "
])
end
这是新测试本身的 .btree 输出:
Tree:
- internal (size 1)
- leaf (size 7)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- key 7
- leaf (size 7)
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
在缩进最少的级别上,我们可以看到根节点(内部节点)。上面写着 size 1,因为它只有一个键。缩进一级,我们看到一个叶节点、一个键和另一个叶节点。根节点中的键(7)是第一个叶节点中的最大键。大于 7 的每个键都位于第二个叶节点中。
一个主要的问题
如果您一直在密切关注,您可能会注意到我们错过了一些重要的事情。看看如果我们尝试插入额外的一行会发生什么:
db > insert 15 user15 person15@example.com
Need to implement searching an internal node
哎呀!谁写的 TODO 消息?:P
下次我们将通过在多级树上实现搜索来继续史诗般的 B-tree 传奇。
译者著
本次代码中移除了表被填充满时的相关代码,因此在测试用例中,我们需要将其移除,以便测试用例可以正常通过,而原文忽略了这一点,如下所示:
- it 'prints error message when table is full' do
- script = (1..1401).map do |i|
- "insert #{i} user#{i} person#{i}@example.com"
- end
- script << ".exit"
- result = run_script(script)
- expect(result[-2]).to eq('db > Error: Table full.')
- end
完整的 diff
diff --git a/db.c b/db.c
index db973cf..4a356bb 100644
--- a/db.c
+++ b/db.c
@@ -138,10 +138,34 @@ const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_SPACE_FOR_CELLS = PAGE_SIZE - LEAF_NODE_HEADER_SIZE;
const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS =
LEAF_NODE_SPACE_FOR_CELLS / LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE;
+const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT = (LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS + 1) / 2;
+const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT =
+ (LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS + 1) - LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+
+/*
+ * Internal Node Header Layout
+ */
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE;
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_OFFSET =
+ INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET + INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE;
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_HEADER_SIZE = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE +
+ INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_SIZE + INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_SIZE;
+
+/*
+ * Internal Node Body Layout
+ */
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_KEY_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t);
+const uint32_t INTERNAL_NODE_CELL_SIZE =
+ INTERNAL_NODE_KEY_SIZE + INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE;
+
+void indent(uint32_t level);
void print_prompt();
void print_row(Row *row);
void print_constants();
-void print_leaf_node(void* node);
+void print_tree(Pager *pager, uint32_t page_num, uint32_t indentation_level);
InputBuffer *new_input_buffer();
void read_input(InputBuffer *input_buffer);
@@ -169,15 +193,38 @@ void cursor_advance(Cursor *cursor);
void *cursor_value(Cursor *cursor);
void initialize_leaf_node(void *node);
+void initialize_internal_node(void *node);
uint32_t *leaf_node_num_cells(void *node);
void *leaf_node_cell(void *node, uint32_t cell_num);
uint32_t *leaf_node_key(void *node, uint32_t cell_num);
void *leaf_node_value(void *node, uint32_t cell_num);
void leaf_node_insert(Cursor *cursor, uint32_t key, Row *value);
Cursor *leaf_node_find(Table *table, uint32_t page_num, uint32_t key);
+void leaf_node_split_and_insert(Cursor *cursor, uint32_t key, Row *value);
NodeType get_node_type(void *node);
void set_node_type(void *node, NodeType type);
+uint32_t get_unused_page_num(Pager *pager);
+uint32_t get_node_max_key(void *node);
+bool is_node_root(void *node);
+void set_node_root(void *node, bool is_root);
+
+void create_new_root(Table *table, uint32_t right_child_page_num);
+uint32_t *internal_node_num_keys(void *node);
+uint32_t *internal_node_right_child(void *node);
+uint32_t *internal_node_cell(void *node, uint32_t cell_num);
+uint32_t *internal_node_child(void *node, uint32_t child_num);
+uint32_t *internal_node_key(void *node, uint32_t key_num);
+
+
+void
+indent(uint32_t level)
+{
+ uint32_t i;
+ for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+}
void
print_prompt()
@@ -203,15 +250,38 @@ print_constants()
}
void
-print_leaf_node(void* node)
-{
- uint32_t i;
- uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
+print_tree(Pager *pager, uint32_t page_num, uint32_t indentation_level)
+{
+ uint32_t i;
+ uint32_t num_keys;
+ uint32_t child;
+ void *node = get_page(pager, page_num);
+
+ switch (get_node_type(node)) {
+ case NODE_LEAF:
+ num_keys = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
+ indent(indentation_level);
+ printf("- leaf (size %d)\n", num_keys);
+ for (i = 0; i < num_keys; i++) {
+ indent(indentation_level + 1);
+ printf("- %d\n", *leaf_node_key(node, i));
+ }
+ break;
+ case NODE_INTERNAL:
+ num_keys = *internal_node_num_keys(node);
+ indent(indentation_level);
+ printf("- internal (size %d)\n", num_keys);
+ for (i = 0; i < num_keys; i++) {
+ child = *internal_node_child(node, i);
+ print_tree(pager, child, indentation_level + 1);
+
+ indent(indentation_level + 1);
+ printf("- key %d\n", *internal_node_key(node, i));
+ }
- printf("leaf (size %d)\n", num_cells);
- for (i = 0; i < num_cells; i++) {
- uint32_t key = *leaf_node_key(node, i);
- printf(" - %d : %d\n", i, key);
+ child = *internal_node_right_child(node);
+ print_tree(pager, child, indentation_level + 1);
+ break;
}
}
@@ -253,7 +323,7 @@ do_meta_command(InputBuffer *input_buffer, Table *table)
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else if (strcmp(input_buffer->buffer, ".btree") == 0) {
printf("Tree:\n");
- print_leaf_node(get_page(table->pager, 0));
+ print_tree(table->pager, 0, 0);
return META_COMMAND_SUCCESS;
} else if (strcmp(input_buffer->buffer, ".constants") == 0) {
printf("Constants:\n");
@@ -321,10 +391,6 @@ execute_insert(Statement *statement, Table *table)
uint32_t num_cells = (*leaf_node_num_cells(node));
uint32_t key_to_insert;
- if (num_cells >= LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS) {
- return EXECUTE_TABLE_FULL;
- }
-
row_to_insert = &statement->row_to_insert;
key_to_insert = row_to_insert->id;
cursor = table_find(table, key_to_insert);
@@ -388,6 +454,7 @@ db_open(const char *filename)
/* New database file. Initialize page 0 as leaf node. */
void *root_node = get_page(pager, 0);
initialize_leaf_node(root_node);
+ set_node_root(root_node, true);
}
return table;
@@ -610,9 +677,18 @@ void
initialize_leaf_node(void *node)
{
set_node_type(node, NODE_LEAF);
+ set_node_root(node, false);
*leaf_node_num_cells(node) = 0;
}
+void
+initialize_internal_node(void *node)
+{
+ set_node_type(node, NODE_INTERNAL);
+ set_node_root(node, false);
+ *internal_node_num_keys(node) = 0;
+}
+
uint32_t *
leaf_node_num_cells(void *node)
{
@@ -645,8 +721,8 @@ leaf_node_insert(Cursor *cursor, uint32_t key, Row *value)
uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(node);
if (num_cells >= LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS) {
/* Node full */
- printf("Need to implement splitting a leaf node.\n");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ leaf_node_split_and_insert(cursor, key, value);
+ return;
}
if (cursor->cell_num < num_cells) {
@@ -697,6 +773,62 @@ leaf_node_find(Table *table, uint32_t page_num, uint32_t key)
return cursor;
}
+void
+leaf_node_split_and_insert(Cursor *cursor, uint32_t key, Row *value)
+{
+ /*
+ * Create a new node and move half the cells over.
+ * Insert the new value in one of the two nodes.
+ * Update parent or create a new parent.
+ */
+
+ int32_t i;
+ void *old_node = get_page(cursor->table->pager, cursor->page_num);
+ uint32_t new_page_num = get_unused_page_num(cursor->table->pager);
+ void *new_node = get_page(cursor->table->pager, new_page_num);
+
+ initialize_leaf_node(new_node);
+
+ /*
+ * All existing keys plus new key should be divided
+ * evenly between old (left) and new (right) nodes.
+ * Starting from the right, move each key to correct position.
+ */
+ for (i = LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE; i >= 0; i--) {
+ uint32_t index_within_node;
+ void *destination;
+ void *destination_node;
+
+ if (i >= LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT) {
+ destination_node = new_node;
+ } else {
+ destination_node = old_node;
+ }
+
+ index_within_node = i % LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+ destination = leaf_node_cell(destination_node, index_within_node);
+
+ if ((uint32_t) i == cursor->cell_num) {
+ serialize_row(value, destination);
+ } else if ((uint32_t) i > cursor->cell_num) {
+ memcpy(destination, leaf_node_cell(old_node, i - 1), LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE);
+ } else {
+ memcpy(destination, leaf_node_cell(old_node, i), LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE);
+ }
+ }
+
+ /* Update cell count on both leaf nodes. */
+ *(leaf_node_num_cells(old_node)) = LEAF_NODE_LEFT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+ *(leaf_node_num_cells(new_node)) = LEAF_NODE_RIGHT_SPLIT_COUNT;
+
+ if (is_node_root(old_node)) {
+ return create_new_root(cursor->table, new_page_num);
+ } else {
+ printf("Need to implement updating parent after split\n");
+ exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ }
+}
+
NodeType
get_node_type(void *node)
{
@@ -711,6 +843,109 @@ set_node_type(void *node, NodeType type)
*((uint8_t *)(node + NODE_TYPE_OFFSET)) = value;
}
+/*
+ * Until we start recycling free pages, new pages will always
+ * go onto the end of the database file.
+ */
+uint32_t
+get_unused_page_num(Pager *pager)
+{
+ return pager->num_pages;
+}
+
+uint32_t
+get_node_max_key(void *node)
+{
+ switch (get_node_type(node)) {
+ case NODE_INTERNAL:
+ return *internal_node_key(node, *internal_node_num_keys(node) - 1);
+ case NODE_LEAF:
+ return *leaf_node_key(node, *leaf_node_num_cells(node) - 1);
+ }
+}
+
+bool
+is_node_root(void *node)
+{
+ uint8_t value = *((uint8_t *) (node + IS_ROOT_OFFSET));
+ return (bool) value;
+}
+
+void
+set_node_root(void *node, bool is_root)
+{
+ uint8_t value = is_root;
+ *((uint8_t *) (node + IS_ROOT_OFFSET)) = value;
+}
+
+void
+create_new_root(Table *table, uint32_t right_child_page_num)
+{
+ /*
+ * Handle splitting the root.
+ * Old root copied to new page, becomes left child.
+ * Address of right child passed in.
+ * Re-initialize root page to contain the new root node.
+ * New root node points to two children.
+ */
+ uint32_t left_child_max_key;
+ void *root = get_page(table->pager, table->root_page_num);
+ void *right_child = get_page(table->pager, right_child_page_num);
+ uint32_t left_child_page_num = get_unused_page_num(table->pager);
+ void *left_child = get_page(table->pager, left_child_page_num);
+
+ /* Left child has data copied from old root. */
+ memcpy(left_child, root, PAGE_SIZE);
+ set_node_root(left_child, false);
+
+ /* Root node is a new internal node with one key and two children. */
+ initialize_internal_node(root);
+ set_node_root(root, true);
+ *internal_node_num_keys(root) = 1;
+ *internal_node_child(root, 0) = left_child_page_num;
+ left_child_max_key = get_node_max_key(left_child);
+ *internal_node_key(root, 0) = left_child_max_key;
+ *internal_node_right_child(root) = right_child_page_num;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_num_keys(void *node)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_NUM_KEYS_OFFSET;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_right_child(void *node)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_RIGHT_CHILD_OFFSET;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_cell(void *node, uint32_t cell_num)
+{
+ return node + INTERNAL_NODE_HEADER_SIZE + cell_num * INTERNAL_NODE_CELL_SIZE;
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_child(void *node, uint32_t child_num)
+{
+ uint32_t num_keys = *internal_node_num_keys(node);
+ if (child_num > num_keys) {
+ printf("Tried to access child_num %d > num_keys %d\n", child_num, num_keys);
+ exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
+ } else if (child_num == num_keys) {
+ return internal_node_right_child(node);
+ }
+
+ return internal_node_cell(node, child_num);
+}
+
+uint32_t *
+internal_node_key(void *node, uint32_t key_num)
+{
+ return internal_node_cell(node, key_num) + INTERNAL_NODE_CHILD_SIZE;
+}
+
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
测试用例。
diff --git a/spec/main_spec.rb b/spec/main_spec.rb
index e649f2d..4cf293f 100644
--- a/spec/main_spec.rb
+++ b/spec/main_spec.rb
@@ -53,15 +53,6 @@ describe 'database' do
])
end
- it 'prints error message when table is full' do
- script = (1..1401).map do |i|
- "insert #{i} user#{i} person#{i}@example.com"
- end
- script << ".exit"
- result = run_script(script)
- expect(result[-2]).to eq('db > Error: Table full.')
- end
-
it 'allows inserting strings that are the maximum length' do
long_username = "a"*32
long_email = "a"*255
@@ -141,10 +132,10 @@ describe 'database' do
"db > Executed.",
"db > Executed.",
"db > Tree:",
- "leaf (size 3)",
- " - 0 : 1",
- " - 1 : 2",
- " - 2 : 3",
+ "- leaf (size 3)",
+ " - 1",
+ " - 2",
+ " - 3",
"db > "
])
end
@@ -166,4 +157,37 @@ describe 'database' do
])
end
+ it 'allows printing out the structure of a 3-leaf-node btree' do
+ script = (1..14).map do |i|
+ "insert #{i} user#{i} person#{i}@example.com"
+ end
+ script << ".btree"
+ script << "insert 15 user15 person15@example.com"
+ script << ".exit"
+ result = run_script(script)
+
+ expect(result[14...(result.length)]).to match_array([
+ "db > Tree:",
+ "- internal (size 1)",
+ " - leaf (size 7)",
+ " - 1",
+ " - 2",
+ " - 3",
+ " - 4",
+ " - 5",
+ " - 6",
+ " - 7",
+ " - key 7",
+ " - leaf (size 7)",
+ " - 8",
+ " - 9",
+ " - 10",
+ " - 11",
+ " - 12",
+ " - 13",
+ " - 14",
+ "db > Need to implement searching an internal node",
+ ])
+ end
+
end